The Viking Age, a period from the late 8th century to the early 11th century, was marked by the seafaring Norse people’s expeditions, raids, and settlements across Europe.
This blog post delves into the Vikings’ significant presence, impact, and legacy in the British Isles, providing a thorough exploration for anyone interested in this fascinating chapter of history.
Introduction
The Vikings, originating from what is now Denmark, Norway, and Sweden, played a crucial role in shaping the history and culture of the British Isles.
Their activities ranged from raiding monasteries to establishing settlements and kingdoms, leaving an indelible mark on the region.
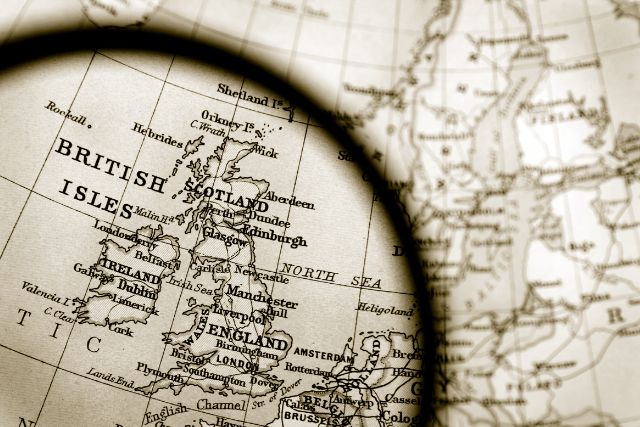

Overview of the Viking Age
The Viking Age is traditionally marked by the Viking raid on the Lindisfarne monastery in 793 AD and ended with the Norman Conquest of England in 1066. During this period, the Vikings were not only warriors but also traders, explorers, and settlers.
The Significance of Viking Raids and Settlements
The Vikings’ raids and settlements in the British Isles were transformative, leading to significant social, political, and cultural changes.
They challenged existing power structures, contributed to the development of new political entities, and influenced art, language, and trade.
The Scope of Viking Activities in the British Isles
The Vikings’ presence in the British Isles was widespread, affecting virtually every region. They established kingdoms in Ireland and Northumbria, raided along the coasts, and settled in various parts of the country, integrating with local populations.
The Early Viking Raids (Late 8th Century to Early 9th Century)
The initial phase of Viking activity in the British Isles was characterized by hit-and-run raids on monasteries and coastal settlements. These raids were swift and often brutal, striking fear into the hearts of the local populations.
The First Viking Raids
The first recorded Viking raid in the British Isles occurred in 793 AD at the Lindisfarne monastery, heralding the beginning of the Viking Age. Monasteries were targeted due to their wealth and relative lack of defenses.
Targets and Tactics
The Vikings primarily targeted monasteries, coastal settlements, and undefended areas. They utilized their advanced seafaring skills and swift, longships to strike quickly and unexpectedly, often retreating before a defensive response could be mustered.
The Raid on Lindisfarne: A Turning Point
The attack on Lindisfarne was a watershed moment, capturing the attention of contemporaries and future generations. It signaled a new kind of threat and highlighted the need for better defenses and a strategic response to Viking raids.
The Great Heathen Army and the Viking Conquests (Mid-9th Century)
The mid-9th century saw a shift from small-scale raids to larger, more organized campaigns, with the arrival of the Great Heathen Army in 865 AD. This force sought not just to plunder, but to conquer and settle.
The Composition and Leadership of the Great Heathen Army
The Great Heathen Army consisted of warriors from different Viking groups, led by notable figures such as Ivar the Boneless and Ubbe Ragnarsson. They were a formidable force, skilled in warfare and strategy.
Major Battles and Conquests
The Army was involved in numerous battles and sieges, including the capture of York in 866 AD. They challenged and overcame local kingdoms, establishing Viking rule over significant portions of the British Isles.


The Establishment of the Danelaw
The Danelaw, a region of England under Viking control, was established in the late 9th century. It was defined by legal and administrative practices distinct from those in Anglo-Saxon-controlled territories.
Viking Settlement and Integration
Over time, Vikings transitioned from raiders and conquerors to settlers, integrating with local populations. They established communities, engaged in trade, and played a significant role in the social fabric of the region.
The Formation of Viking Communities
Viking settlements were established across the British Isles, including significant urban centers like York and Dublin. These communities were hubs of trade, craftsmanship, and cultural exchange.
Cultural Exchanges and Integration
The Vikings and the local populations influenced each other’s cultures, practices, and languages. Norse words were incorporated into English, and the Vikings adopted elements of local customs and governance.
The Impact on Local Societies
The Vikings’ presence led to changes in military tactics, trade practices, and governance. They also contributed to the cultural diversity of the region, leaving a lasting legacy.
The Viking Kingdoms in the British Isles
The Vikings established several kingdoms and territories in the British Isles, exerting their influence and governance over these regions.


The Kingdom of York
The Kingdom of York was one of the most significant Viking territories, established following the capture of the city in 866 AD. It was a major political and trade center, playing a crucial role in the Viking presence in England.
The Kingdom of Dublin
Dublin, founded by the Vikings in the 9th century, became a major trade hub and the center of Norse power in Ireland. It was one of the most important Viking settlements in the British Isles.
Other Viking Kingdoms and Territories
In addition to York and Dublin, there were other Viking territories and kingdoms throughout the British Isles, each playing a unique role in the regional dynamics of the Viking Age.
The Decline of Viking Power and Influence
By the late 10th and early 11th centuries, Viking power in the British Isles began to wane. This decline was due to a combination of external pressures, internal conflicts, and changing political landscapes.
The Role of External Conflicts
The Vikings faced challenges from emerging powers, including the growing strength of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms and external threats from other Viking groups. These conflicts weakened their hold on territories.
Internal Struggles and the Loss of Territories
Internal strife, succession disputes, and challenges to Viking rule also contributed to the decline of their power in the British Isles. Territories were lost, and influence diminished.
The Norman Conquest and the End of the Viking Age
The Norman Conquest of England in 1066 marked the end of the Viking Age. The Normans, themselves of Viking descent, brought a new era of governance and culture, integrating and transforming the existing Viking influences.
Viking Legacy and Cultural Impact
The Vikings left a profound legacy in the British Isles, influencing language, culture, governance, and more. Their impact continues to be felt and studied today.
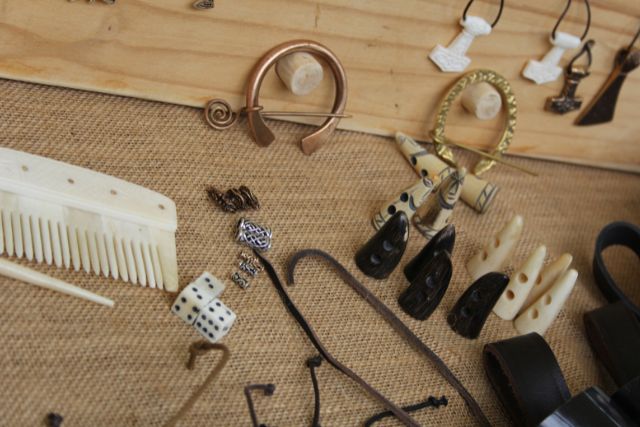


Archaeological Findings and Artifacts
Archaeological excavations have uncovered a wealth of Viking artifacts and remnants of settlements, providing invaluable insights into their lives, culture, and activities in the British Isles.
The Influence on Language and Place Names
The Norse language has left a lasting imprint on English, particularly in place names and vocabulary. Words like “sky” and “window” have Norse origins, and many place names in former Viking territories reflect this heritage.
The Enduring Fascination with Vikings
The Vikings continue to captivate the public imagination, with their history and culture explored in books, films, and television shows. They remain a subject of fascination and study, reflecting their enduring legacy.
Conclusion
The Vikings played a transformative role in the history of the British Isles, leaving a legacy that is still evident today. Their impact on culture, language, and governance has shaped the region in profound ways.
Summary of Key Points
This blog post has explored the Vikings’ raids, settlements, and kingdoms in the British Isles, highlighting their impact, legacy, and the factors contributing to their decline. The Vikings’ influence is a testament to their significant role in the region’s history.
The Continuing Importance of Viking History in the British Isles
Understanding Viking history enriches our knowledge of the past, providing context and insights into the development of the British Isles. It reminds us of the complex interplay of cultures and the lasting impacts of historical events.