Vikings, known for their formidable presence across seas, have left an indelible mark on history.
Their routes across the oceans have been a subject of fascination and study, revealing a complex understanding of navigation and mapping in a time before modern technology.
The Historical Context of Viking Journeys
The era known as the Viking Age, spanning approximately from 793 to 1066 AD, was a time of exploration, warfare, and trade for the Norse people.
Their journeys were not merely raids but also quests for trade, settlement, and exploration.


Understanding the Viking Age
The Viking Age was characterized by the Norse people’s expansion from their Scandinavian homelands.
Their voyages spanned from the shores of North America to the Caspian Sea in Asia, demonstrating their remarkable adaptability and curiosity.
The Vikings’ reputation as warriors is well-documented, but their roles as traders and explorers are equally significant.
Significance of Sea Voyages in Viking Culture
For the Vikings, sea voyages were central to their way of life. The sea was a highway that connected distant lands, and mastery over it was a matter of survival and prosperity.
Their maritime skills were a source of pride and were deeply embedded in their myths and legends.
Unveiling the Viking Longship: The Vessel of Discovery
The Viking longship, with its iconic silhouette, was the heart of Norse exploration.
These vessels were marvels of their time, built for speed, agility, and durability, capable of navigating both high seas and shallow rivers.
Design and Features of Longships
Longships were crafted with a clinker-built technique, where planks were overlapped and riveted together, creating a light but sturdy frame.
Their symmetrical bow and stern allowed for swift reversals in direction, which was particularly useful during raids and landings.
Advancements in Shipbuilding Techniques
The construction of longships reflected the Vikings’ advanced understanding of shipbuilding.
They were able to produce vessels that were not only sea-worthy but could also carry significant cargo, facilitating extensive trade and the establishment of settlements in far-flung areas.
Deciphering the Viking Compass: Tools of Navigation
While the Vikings did not have the magnetic compass, they had a variety of tools and techniques at their disposal for navigation, which enabled them to voyage across vast and open seas with surprising accuracy.
Secrets of the Viking Cartography: Mapping the Unknown
The Vikings may not have had maps in the modern sense, but they certainly understood their landscape and seascape.
They left behind a wealth of information in the form of sagas, rune stones, and even navigation aids that offer insight into how they viewed and traversed their world.
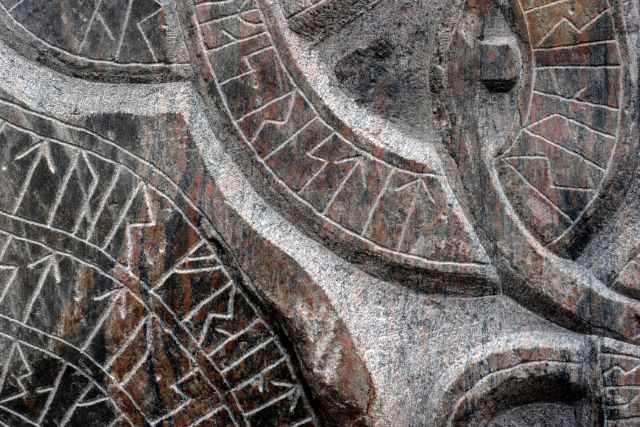


Understanding Viking Maps and Runes
It is believed that the Vikings used landmarks, stories, and possibly even carved maps for navigation.
Runes, the Viking alphabet, may have been used to describe routes and directions, as evidenced by rune stones that sometimes depicted journey narratives or territorial boundaries.
Analysing Historical Viking Maps and Their Accuracy
While no maps from the Viking Age have survived, there is evidence to suggest that they made and used them.
The accuracy of Viking ‘maps’ can be inferred from their successful navigation, indicating they had a practical understanding of geography and could convey it to others.
Famous Viking Routes and Their Discoveries
The Vikings were prolific explorers, and their routes are the stuff of legend.
From their homelands in Scandinavia, they reached the far corners of the North Atlantic, ventured along the rivers of Eastern Europe, and even set foot on North American shores.
Exploring the Western Routes: To Greenland and Beyond
The western voyages of the Vikings took them to the far reaches of the North Atlantic.
Greenland, Iceland, and even the shores of North America were among their destinations, as they sought new lands for settlement and resources.
The Eastern Trails: The Volga and Dnieper Trade Routes
Eastward, the Vikings traveled along the river systems of Russia, utilizing the Volga and Dnieper rivers.
These routes allowed them to trade with the Byzantine Empire and the Arab Caliphates, bringing silk, spices, and other luxuries back to the Norse world.

Legacy of Viking Navigators: Influences and Innovations
The Vikings were not only explorers and warriors, they were also innovators.
Their legacies in navigation have provided a foundation for modern techniques and have left a lasting impact on seafaring practices.
The Sagas: Storytelling and Geographical Descriptions
The sagas, Norse historical narratives, contain a wealth of geographical information.
They describe lands visited by the Vikings, weather patterns, and navigation routes, often with remarkable detail that historians and archaeologists have been able to corroborate.
Viking Contributions to Modern Navigation Techniques
Although they did not leave behind technical manuals, the navigational strategies of the Vikings, such as the use of the sunstone, have been studied and appreciated for their ingenuity.
These techniques are seen as precursors to some of the tools in navigation used before the advent of GPS technology.
Navigating Like a Viking: Techniques and Reenactments
Today, historians, archaeologists, and enthusiasts strive to understand and replicate the Vikings’ mastery of the seas.
Through experimental archaeology and practical application, they seek to rediscover the techniques that allowed the Vikings to traverse the North Atlantic with such success.
Modern Experiments in Viking Navigation
Modern experiments in Viking navigation involve building replicas of Viking ships and sailing them using the same tools and techniques that would have been available during the Viking Age.
These experiments have shed light on the practical aspects of Viking navigation methods.
Recreating Viking Journeys in the 21st Century
Reenactments of Viking journeys have been undertaken by enthusiasts around the world, often resulting in valuable insights into the challenges and realities of Viking sea travel.
These endeavors honor the Viking spirit of adventure and bring history to life for a modern audience.
Preserving Viking Heritage: Conservation and Education
Preservation of Viking heritage is crucial not just for historical understanding, but for cultural identity.
Conservation efforts are underway across the world to maintain and protect Viking sites and artifacts, including their ships and the rare evidence of their mapping and navigation tools.


Protecting Ancient Viking Maps and Artefacts
Efforts to protect Viking artifacts, such as rune stones and ship remnants, involve meticulous conservation work.
Museums and historical societies play a key role in these efforts, ensuring that these ancient items are preserved for future generations to study and appreciate.
Educational Programs and Interactive Learning
Educational programs that focus on Viking history, especially their navigation and mapping techniques, are essential in bringing this aspect of history to life.
Interactive learning experiences, such as simulated voyages and map-making workshops, allow learners to get a hands-on understanding of Viking culture.
Conclusion: The Enduring Fascination with Viking Journeys
The fascination with Vikings and their seafaring achievements continues to capture the imagination of people around the world.
Their ability to navigate vast and treacherous waters with the technology of their time is a testament to their resilience and ingenuity.
Reflections on the Viking Spirit of Adventure
The Viking spirit of adventure and exploration is something that resonates with many today.
Their bold voyages into the unknown reflect a human yearning for discovery and understanding, which continues to inspire adventurers and scholars alike.
The Continuing Legacy in Popular Culture
The legacy of the Vikings, especially their navigational achievements, lives on in popular culture.
From literature to television to video games, the Viking ethos of exploration and conquest endures. Intriguing and inspiring new generations with their storied past.











