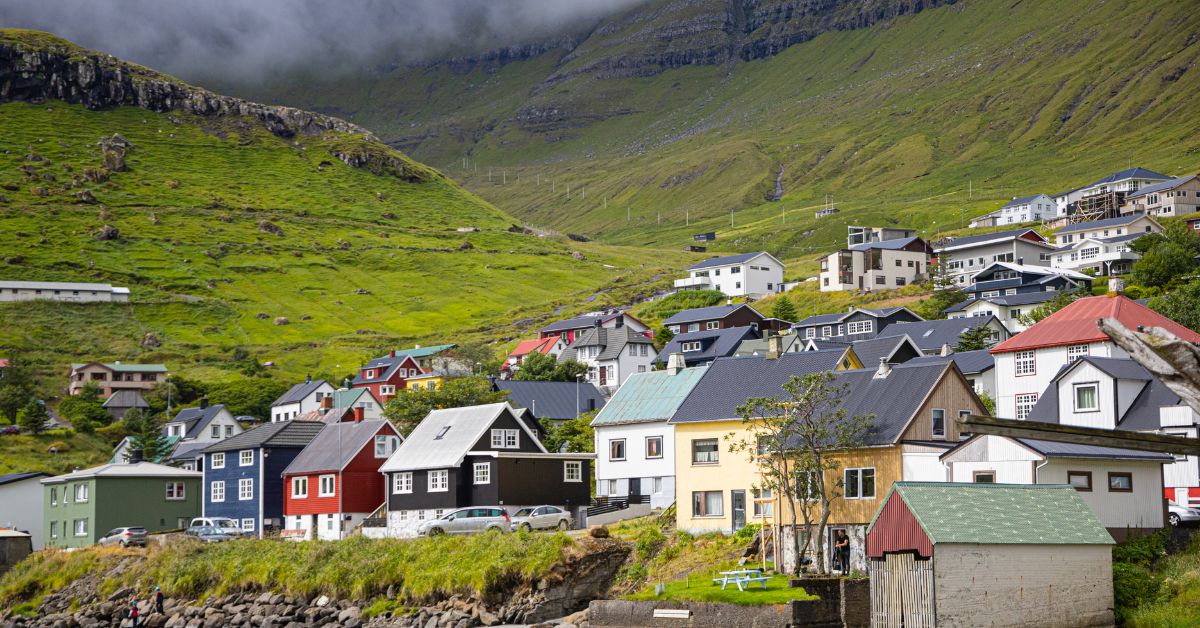
The Faroe Islands, located in the North Atlantic, are a fascinating chapter in Viking history.
These remote islands became a significant outpost for Norse explorers, settlers, and traders during the Viking Age.
This post delves into the rich history, culture, and legacy of the Vikings in the Faroe Islands, providing an in-depth look at their impact on these rugged islands.
Introduction
The Faroe Islands, an archipelago of 18 islands, are situated between Norway and Iceland. Their strategic location made them a prime target for Viking explorers seeking new lands and resources.
The islands’ dramatic landscapes, with steep cliffs, grassy meadows, and a harsh climate, posed both challenges and opportunities for the Norse settlers.

Geographical Overview
Located in the North Atlantic Ocean, the Faroe Islands are known for their rugged terrain and volatile weather.
The islands are characterized by their steep cliffs, fjords, and rolling hills, providing both natural beauty and formidable challenges for early settlers.
Despite the harsh conditions, the fertile soil of the islands and abundant marine life made them an attractive destination for Viking explorers.
Historical Significance
The Faroe Islands played a crucial role in the expansion of Viking territories. As an outpost, the islands served as a waypoint for voyages between Scandinavia, Iceland, and Greenland.
The settlement of the Faroes marked a significant step in the Vikings’ exploration and colonization of the North Atlantic.
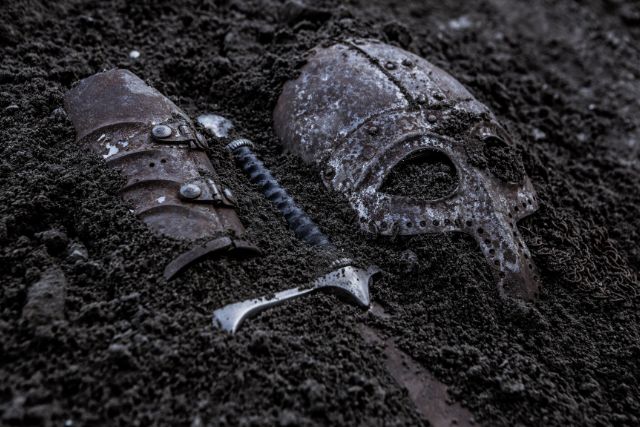
Early Norse Settlers
The first Norse settlers arrived in the Faroe Islands during the early 9th century.
These pioneers were drawn by the promise of new lands and the opportunity to escape political turmoil in their homelands.
The sagas tell the tale of Grímur Kamban, believed to be the first Viking to set foot on the islands.
The Journey of Grímur Kamban
According to the sagas, Grímur Kamban fled Norway to escape the consolidation of power under King Harald Fairhair. He and his crew landed on the Faroe Islands around the early 800s.
The name Kamban suggests Gaelic origins, indicating possible connections with Viking settlements in Ireland.
Grímur’s adventurous spirit led to the establishment of the first permanent Norse settlement on the islands.
First Viking Settlements
The initial Viking settlements were small but grew steadily as more Norse explorers arrived. The settlers brought with them their traditions, culture, and agricultural practices.
They established farms, built homes, and adapted to the islands’ challenging environment. The settlement of Tórshavn, founded during this period, would later become the Faroese capital.


Interaction with Celtic Inhabitants
Historical evidence suggests that Celtic monks may have visited the Faroe Islands before the Vikings.
The interaction between the Norse settlers and any existing inhabitants remains a topic of debate among historians.
However, the Vikings’ arrival marked the beginning of a new era for the islands, characterized by Norse culture and governance.
Viking Society and Economy
The Viking society in the Faroe Islands was primarily agrarian, with settlers focusing on farming and animal husbandry.
The islands’ economy relied heavily on agriculture, trade, and resourcefulness in adapting to the local environment.
Agriculture and Livestock Management
The Norse settlers introduced various crops and livestock to the Faroe Islands. They cultivated barley and hay, essential for sustaining their livestock through the harsh winters.
Sheep farming became a cornerstone of the Faroese economy, giving the islands their name, which means “Sheep Islands” in Old Norse.
In addition to sheep, the settlers raised goats, pigs, and cows, ensuring a stable food supply.
Trade and Economic Networks
Despite their remote location, the Faroe Islands maintained trade connections with Norway and other Viking territories.
Archaeological finds indicate that Faroese settlers traded goods such as wool, fish, and animal products with the mainland.
These trade networks helped the islands thrive and integrate into the broader Viking world.
Daily Life of Viking Settlers
Life in the Faroe Islands was challenging but manageable for the Viking settlers. They built robust longhouses from local materials, designed to withstand the harsh weather.
Daily activities included farming, fishing, and crafting. The settlers also engaged in social and political activities, gathering at the Løgting, one of the oldest parliamentary institutions in the world.


Political Structures
The Vikings established a structured political system in the Faroe Islands, modeled after other Norse societies.
The Løgting, a proto-parliament, played a crucial role in governance and community decision-making.
Establishment of the Løgting
The Løgting was established in Tórshavn, providing a forum for free men to discuss and decide on communal matters.
This early form of democracy allowed settlers to have a say in their governance, fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility.
Comparison with the Althing in Iceland
The Faroese Løgting shares similarities with the Icelandic Althing, both being early examples of parliamentary systems.
These institutions highlight the Vikings’ innovative approach to governance, emphasizing community participation and legal frameworks.
Role of Free Men in Governance
In Viking society, free men had significant rights and responsibilities.
They participated in the Løgting, contributing to the legislative process and ensuring that decisions reflected the community’s needs and values.
This democratic tradition underscored the Vikings’ commitment to collective governance.
Cultural and Religious Transformation
The cultural landscape of the Faroe Islands underwent significant changes with the arrival of Christianity. This religious shift had a profound impact on the Viking settlers and their traditions.


The Arrival of Christianity
Christianity began to spread in the Faroe Islands during the 10th century. The new faith gradually replaced the Old Norse religion, bringing with it new cultural practices and beliefs.
The introduction of Christianity was a pivotal moment in Faroese history, influencing all aspects of life.
Sigmundur Brestisson and the Conversion of the Faroes
Sigmundur Brestisson, a notable Viking chieftain, played a key role in converting the Faroese to Christianity.
Sent by the Norwegian King Olaf Tryggvason, Brestisson faced resistance but ultimately succeeded through a combination of persuasion and force.
His efforts marked the beginning of a new religious era on the islands.
Impact of Christianity on Viking Traditions
The spread of Christianity significantly altered Viking traditions and practices. Pagan rituals and beliefs were gradually replaced by Christian customs.
Churches were built, and Christian festivals became part of the Faroese cultural fabric. This transformation marked the end of the Viking Age in the Faroe Islands but left a lasting legacy.
Historical and Archaeological Sites
The Faroe Islands are home to numerous historical and archaeological sites that offer insights into the Viking era. These sites are a testament to the islands’ rich history and cultural heritage.


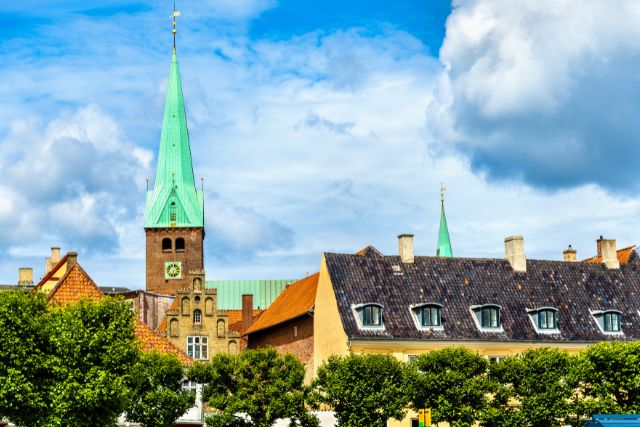
Kirkjubøur: The Ecclesiastical Center
Kirkjubøur, located on the southern tip of Streymoy, was a significant ecclesiastical center during the Middle Ages.
The village was home to the Bishop’s residence and played a central role in the religious life of the islands.
Today, Kirkjubøur remains a key historical site, attracting visitors interested in its Viking and medieval heritage.
St. Magnus Cathedral and St. Olav’s Church
St. Magnus Cathedral, built in the 1300s, and St. Olav’s Church, dating back to 1111, are among the most important religious sites in the Faroe Islands.
The cathedral, now in ruins, once served as the ecclesiastical seat of power. St. Olav’s Church, with its medieval carvings, remains a testament to the islands’ Christian heritage.


Roykstovan: One of the Oldest Inhabited Timber Houses
Roykstovan, part of the Kirkjubøargarður farm, is one of the oldest inhabited timber houses in the world.
Dating back to the 12th century, this turf-roofed building offers a glimpse into medieval Faroese life.
The farm has been continuously inhabited by the same family for generations, preserving its historical significance.
The Lasting Legacy of Viking Heritage
The Viking heritage of the Faroe Islands continues to influence modern Faroese culture. The islands’ history is reflected in their traditions, architecture, and cultural practices.
Modern Faroese Culture and Traditions
Today, the Faroe Islands celebrate their Viking heritage through festivals, historical reenactments, and cultural events.
These traditions keep the spirit of the Viking Age alive, fostering a sense of pride and identity among the Faroese people.


Preservation of Viking Architecture and Landmarks
Efforts to preserve Viking architecture and landmarks are ongoing in the Faroe Islands.
Sites like Kirkjubøur, Tórshavn, and various archaeological finds are protected and maintained to ensure their historical value is not lost.
These preservation efforts highlight the importance of the Viking legacy in the islands’ cultural heritage.
Connecting the Past to the Present
The Faroe Islands’ Viking heritage continues to shape the islands’ identity today. From place names to cultural practices, the legacy of the Norse settlers is woven into the fabric of Faroese society.
Modern Faroese people maintain a deep connection to their Viking ancestors, celebrating this heritage through various cultural expressions and community events.
Conclusion
The Faroe Islands stand as a testament to the enduring legacy of the Viking Age.
The islands’ history is marked by the adventurous spirit of Norse settlers, the establishment of a democratic society, and the profound cultural shifts brought about by the arrival of Christianity.
This comprehensive exploration of the Faroe Islands’ Viking heritage provides a detailed understanding of their historical significance and lasting impact.


Summary of Viking Impact on the Faroe Islands
The Viking impact on the Faroe Islands is evident in the islands’ political structures, agricultural practices, and cultural traditions.
The establishment of settlements, the development of the Løgting, and the introduction of Christianity are key aspects of this legacy.
The islands’ history is rich with stories of exploration, adaptation, and transformation.
Invitation to Explore Further
For those intrigued by the Viking history of the Faroe Islands, there is much more to discover.
Visiting the islands offers an opportunity to explore historical sites, experience local traditions, and connect with the enduring spirit of the Vikings.
Dive deeper into this fascinating chapter of history by exploring the resources available on vikingsrule.com.











