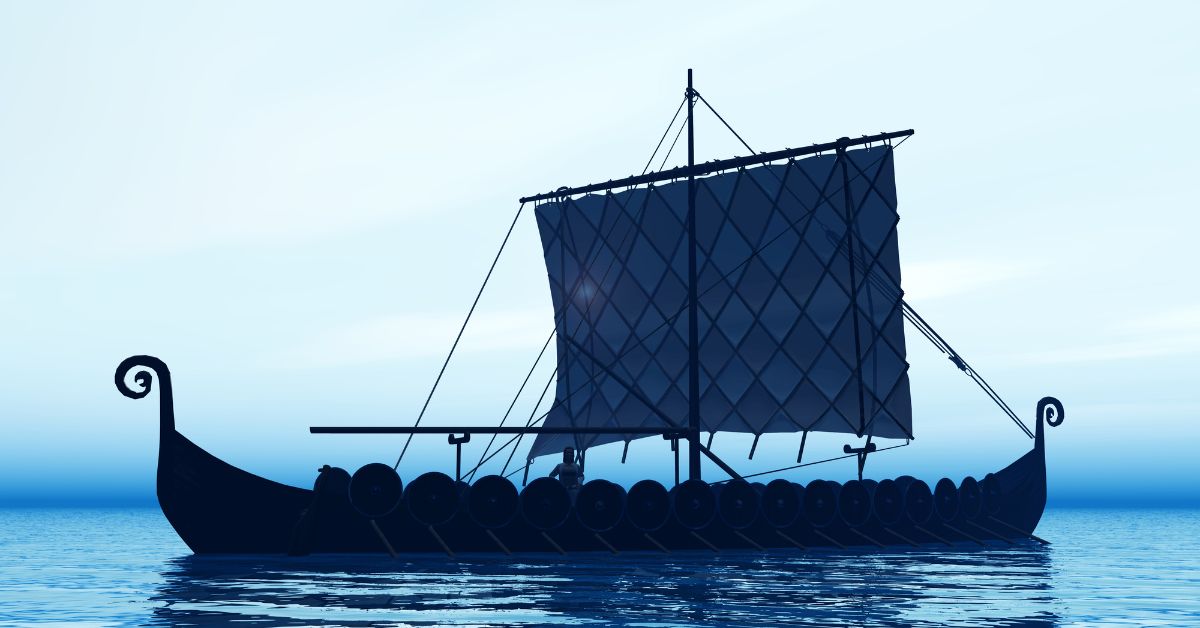
The Viking longship stands as a testament to the ingenuity and maritime prowess of the Norsemen.
These ships were not only pivotal in the Viking Age but also represented the pinnacle of naval technology during their time.
This blog post delves into the fascinating technology behind these legendary vessels, exploring their design, construction, navigation techniques, and their broader impact on Viking society and history.
Introduction
Viking longships were renowned for their speed, versatility, and durability.
They enabled the Vikings to explore, trade, and conduct raids across vast distances, from the coasts of North America to the rivers of Eastern Europe.
This comprehensive guide examines the technological marvels that made these ships so effective and feared.
The Origins of Viking Longships
The development of Viking longships can be traced back to earlier Scandinavian boat-building traditions.
These vessels evolved from simpler designs into sophisticated ships capable of navigating both open seas and shallow rivers.


The Evolution of Viking Maritime Technology
Early Scandinavian boats were constructed using basic materials and techniques. However, as the need for more robust and versatile vessels grew, so did the complexity of their construction.
The Vikings borrowed and improved upon shipbuilding techniques from other cultures, leading to the creation of the longship.
Early Influences and Innovations
The longship’s design was influenced by earlier European and Mediterranean seafaring technologies.
Innovations such as the clinker-built method and the use of iron rivets were crucial in the evolution of these ships.
These advancements allowed for stronger, more flexible hulls that could withstand the harsh conditions of the North Atlantic.
Design and Construction
The Viking longship’s design and construction were central to its success.
These ships were built to be fast, durable, and versatile, capable of navigating various waters and carrying out different types of missions.
Materials Used in Longship Construction
The primary material used in constructing Viking longships was oak. This wood was chosen for its strength and durability, making it ideal for the rough seas encountered by the Vikings.
Selection of Timber
Carpenters selected oak trees with the right curvature for different parts of the ship. The natural bend of the wood provided additional strength and flexibility to the hull.
Iron Rivets and Fastenings
Iron rivets were used to fasten the overlapping planks of the hull. This method, known as clinker-building, created a strong yet flexible structure that could absorb the impact of waves without breaking.
Clinker-Built Method
The clinker-built method involved overlapping planks of wood, fastened together with iron rivets. This technique was crucial in creating a durable and flexible hull.
Overlapping Planks
Each plank overlapped the one below it, creating a stepped pattern. This design allowed the hull to flex with the waves, reducing the risk of cracking.
Flexibility and Strength
The overlapping planks and the use of iron rivets provided both flexibility and strength. This construction method made the longship resilient to the harsh conditions of open sea voyages.
Shape and Features of the Longship
The shape and features of the Viking longship were designed to optimize speed, maneuverability, and versatility. These attributes made them formidable in both exploration and warfare.
Shallow Draft for Versatility
The longship’s shallow draft allowed it to navigate shallow waters and rivers. This feature enabled the Vikings to raid inland settlements and escape quickly.
Narrow and Long Design
The long, narrow design of the longship reduced water resistance, making it faster and more maneuverable. This design also made the ship more stable in rough seas.
Versatility in Use
Viking longships were versatile vessels, used for both war and trade. Their design allowed them to perform a variety of tasks efficiently.
Warships vs. Trade Ships
While some longships were designed specifically for warfare, others were built for trade. Warships were lighter and faster, while trade ships were larger and could carry more cargo.


Adaptability for Different Waters
The design of the longship allowed it to navigate both open seas and shallow rivers. This adaptability was crucial for the Vikings, who often needed to travel through diverse waterways.
Navigation Techniques
The Vikings were skilled navigators, using a combination of natural elements and innovative tools to find their way across vast distances.
Their navigation techniques were critical to their success as explorers and raiders.
Natural Elements for Navigation
The Vikings relied on natural elements such as the sun, stars, and waves to navigate. These methods were simple yet effective, allowing them to travel great distances with remarkable accuracy.
Sunstones and Solar Navigation
Sunstones, a type of calcite crystal, were used to locate the sun on cloudy days. By holding the stone up to the sky, the Vikings could determine the sun’s position and navigate accordingly.


Using Stars, Waves, and Wind
At night, the Vikings used the stars to guide their way. They also observed wave patterns and wind directions to stay on course. These natural cues were essential for long-distance navigation.
Innovative Tools and Methods
In addition to natural elements, the Vikings developed innovative tools and methods to aid their navigation. These techniques enhanced their ability to travel safely and efficiently.
Birds and Ravens for Land Detection
The Vikings often carried birds, such as ravens, on their voyages. When released, these birds would fly towards land, helping the crew determine the direction of the nearest shore.
Wave and Wind Patterns
Experienced Viking navigators could interpret wave and wind patterns to predict weather changes and navigate more effectively.
This knowledge was passed down through generations, ensuring the safety and success of their voyages.
Functionality and Performance
The functionality and performance of Viking longships were unmatched during their time.
These ships were designed to be fast, maneuverable, and capable of handling various missions, from exploration to warfare.
Speed and Maneuverability
Speed and maneuverability were critical features of the Viking longship. These attributes allowed the Vikings to conduct swift raids and evade pursuit, making them formidable adversaries.
Combined Use of Sails and Oars
Longships were equipped with both sails and oars, allowing them to achieve high speeds. The combination of wind and human power made these ships incredibly fast and agile.


Rowing Techniques and Crew Management
The Vikings developed efficient rowing techniques and crew management practices. Rowers worked in shifts, ensuring that the ship could maintain speed over long distances without exhausting the crew.
Open Sea Capabilities
Viking longships were capable of handling open sea voyages, thanks to their sturdy construction and advanced navigation techniques. These ships could cross vast distances, reaching far-flung destinations.
Crossing the North Atlantic
The Vikings used their longships to cross the North Atlantic, reaching places like Iceland, Greenland, and even North America.
Their ability to navigate these treacherous waters was a testament to the ship’s design and the crew’s skill.
Adapting to Mediterranean Conditions
Longships were also used in the Mediterranean, where they had to adapt to different water conditions. Their versatility allowed the Vikings to conduct raids and trade missions in a variety of environments.
Cultural and Societal Impact
The Viking longship had a profound impact on Viking culture and society. These ships were not only tools of war and trade but also symbols of power and prestige.
Role in Viking Raids and Warfare
The longship was a key element in Viking raids and warfare. Its speed and agility made it ideal for surprise attacks, allowing the Vikings to strike swiftly and retreat before their enemies could respond.
Hit-and-Run Tactics
Viking raids often employed hit-and-run tactics. The longship’s design enabled quick landings and departures, making it difficult for enemies to mount a defense.


Psychological Impact on Enemies
The sight of a Viking longship on the horizon struck fear into the hearts of many. The psychological impact of these ships, combined with the Vikings’ reputation for ferocity, made them a formidable force.
Trade and Economic Influence
Longships also played a crucial role in Viking trade and economics. These ships facilitated the movement of goods and people, helping to establish trade networks and settlements.
Facilitating Long-Distance Trade
Viking longships enabled long-distance trade, connecting Scandinavia with distant markets in Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. This trade brought wealth and resources back to Viking homelands.
Connecting Viking Territories
The longships helped to connect the scattered Viking territories, creating a network that facilitated communication and trade. This connectivity was crucial for maintaining political control and fostering economic growth.
Political and Social Significance
Longships were more than just tools for the Vikings; they were symbols of power and prestige. Their construction and use were deeply intertwined with the social and political structures of Viking society.
Strengthening Scandinavian Kingdoms
The use of longships helped strengthen the Scandinavian kingdoms by enabling rapid military mobilization and efficient control over large territories.
These ships allowed Viking leaders to project power and influence across vast regions.
Symbolism in Viking Society
Longships were often featured in Viking art and literature, symbolizing the strength and adventurous spirit of the Norse people.
They were also used in elaborate burial rituals, highlighting their importance in Viking culture.
Case Studies of Notable Longships
Several notable longships have been discovered and studied, providing valuable insights into Viking shipbuilding techniques and their historical significance. Here are a few examples:
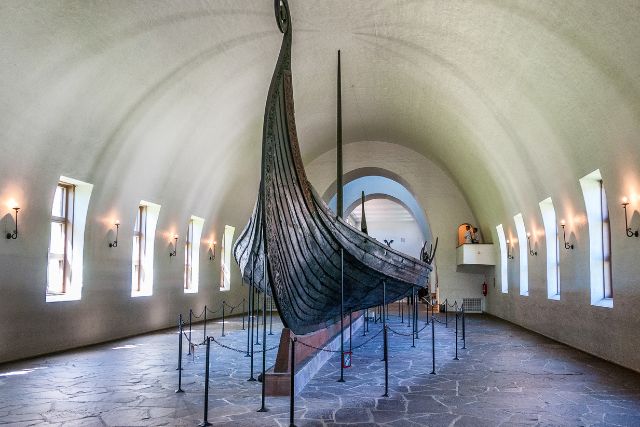
The Gokstad Ship
The Gokstad ship is one of the best-preserved Viking longships, discovered in a burial mound in Norway.
This ship offers a wealth of information about Viking construction techniques and their maritime capabilities.
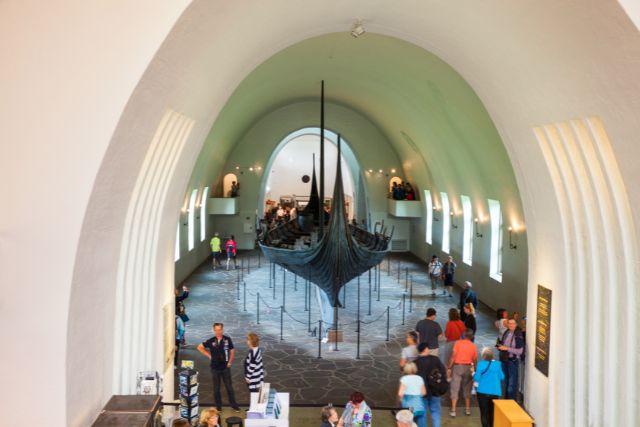


Construction and Features
The Gokstad ship was built around 890 AD and measures approximately 23.5 meters in length and 5.2 meters in width.
It was constructed using the clinker-built method, with overlapping oak planks and iron rivets, providing both strength and flexibility.
Historical Significance
The Gokstad ship was used for both warfare and trade, reflecting the dual-purpose design of Viking longships.
Its discovery has provided archaeologists with critical insights into Viking shipbuilding and maritime practices.
The Oseberg Ship
The Oseberg ship is another remarkable Viking longship, known for its elaborate decoration and historical significance.
Discovered in a burial mound in Norway, this ship provides a glimpse into the artistry and craftsmanship of the Viking Age.
Construction and Features
The Oseberg ship was built around 820 AD and measures approximately 21.5 meters in length and 5 meters in width.
It features intricate carvings on the prow and stern, showcasing the artistic talents of Viking craftsmen.
Archaeological Discoveries
The Oseberg ship was discovered in 1904, buried with numerous artifacts, including tools, textiles, and a richly decorated cart.
These findings have provided valuable insights into Viking burial customs and daily life.


The Sea Stallion from Glendalough
The Sea Stallion from Glendalough is a modern reconstruction of a Viking longship, based on the Skuldelev 2 ship discovered in Denmark.
This project has provided researchers with practical experience in Viking shipbuilding and sailing techniques.
Reconstruction and Trial Voyages
The Sea Stallion was built using traditional Viking techniques and materials.
It has been used in several trial voyages, allowing researchers to test its performance and gather data on Viking navigation and maritime practices.
Insights from Modern Experiments
The trial voyages of the Sea Stallion have confirmed the effectiveness of Viking longships in various conditions.
These experiments have demonstrated the ships’ speed, maneuverability, and seaworthiness, validating historical accounts of their capabilities.
Conclusion
The technology behind the Viking longship was a marvel of its time, combining advanced construction techniques with practical innovations.
These ships were instrumental in the Vikings’ ability to explore, trade, and conquer, leaving a lasting legacy on maritime history.
The detailed study of longships like the Gokstad, Oseberg, and modern reconstructions like the Sea Stallion continues to shed light on the remarkable achievements of Viking shipbuilders.