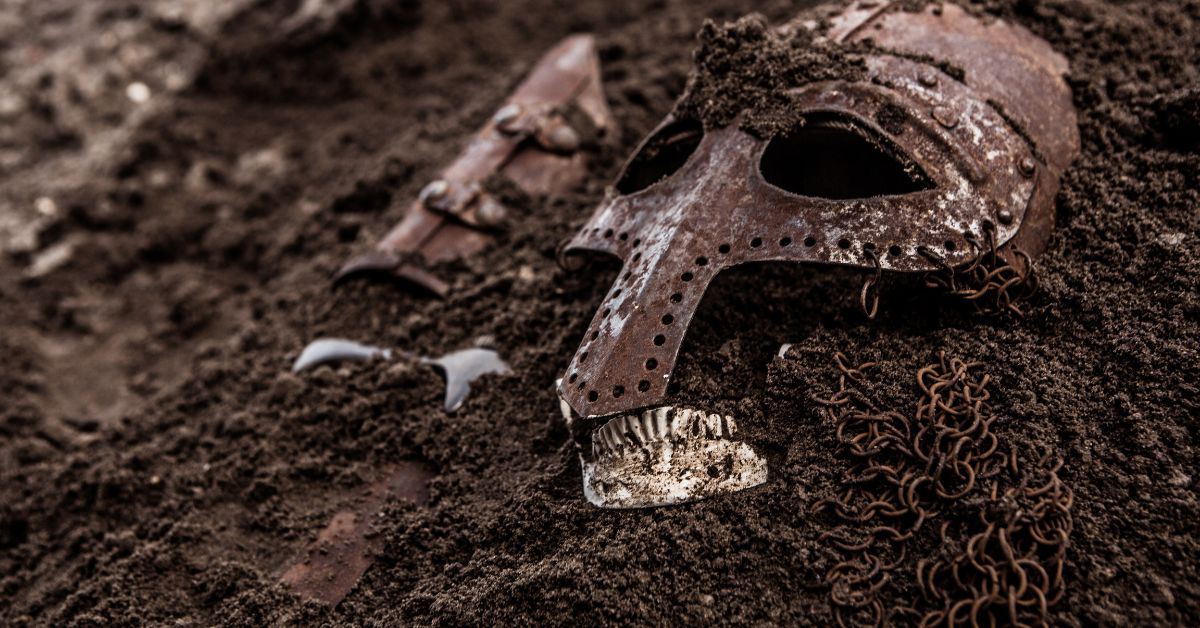
The Vikings, known for their fearless explorations and warrior ethos, also had intricate customs surrounding death and burial.
These practices were deeply connected to their beliefs about the afterlife and societal status. Understanding these customs offers a fascinating glimpse into Viking society and their worldview.
The Significance of Death in Viking Culture
In Viking culture, death was not merely an end but a transition to another existence. The way they treated the dead reflected their beliefs about the afterlife and the individual’s standing in life.
Beliefs About the Afterlife
Vikings believed in an afterlife where the soul’s journey continued. The destination depended largely on how one lived and died.
Valhalla and Hel
Valhalla, ruled by Odin, was the hall of slain warriors who died heroically in battle. These warriors, known as the Einherjar, spent their days preparing for Ragnarok, the end of the world.
Hel, on the other hand, was the realm of those who died of sickness or old age. It was a place of rest rather than punishment, ruled by the goddess Hel.


The Journey to the Afterlife
The journey to the afterlife was seen as a voyage, often symbolized by the burial ship. This belief was reflected in the meticulous preparation of the dead, aimed at equipping them for this final journey.
Social Status and Funeral Rites
Social status played a significant role in determining the type and grandeur of Viking funerals. High-status individuals received elaborate send-offs, while common folk had simpler rites.
High-Status Funerals
For the elite, funerals were grand events, often involving ship burials, extensive grave goods, and elaborate rituals. These practices highlighted their achievements and ensured their legacy.
Common Folk Burials
Commoners were typically buried in simpler graves, often in wooden chambers or earth pits. Despite the lack of grandeur, these burials still reflected the community’s respect and the individual’s role in life.
Types of Viking Burials
Viking burials varied widely, influenced by regional practices and the deceased’s status. The types of burials ranged from ship burials to cremations and mound burials.
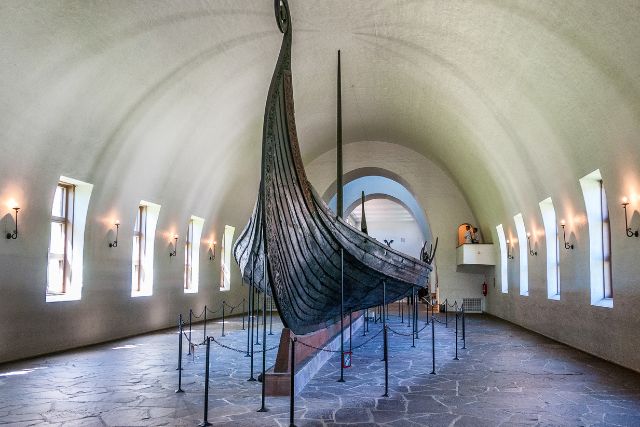
Ship Burials
Ship burials were among the most iconic and reserved for the most esteemed individuals. These burials involved placing the deceased in a ship, along with grave goods, and either setting it ablaze or burying it.
Famous Ship Burials
Several notable ship burials have been discovered, providing insight into this practice.
The Oseberg Ship
The Oseberg ship burial, discovered in Norway, is one of the most spectacular finds.
It contained the remains of two high-status women and a wealth of grave goods, reflecting their significant roles in society.
The Gokstad Ship
The Gokstad ship, also found in Norway, held the remains of a male chieftain. This burial included numerous weapons, tools, and animals, showcasing the importance of the deceased.


Symbolism and Significance
The ship symbolized a journey, reflecting the Viking belief in the soul’s voyage to the afterlife. These burials were not just final resting places but statements of power and prestige.
Cremation Practices
Cremation was a common practice among Vikings, believed to purify the dead and help their spirits ascend to the afterlife. This practice was often accompanied by elaborate rites and ceremonies.
Rituals and Procedures
Cremations typically involved a funeral pyre, where the body was burned along with grave goods. The ashes were then collected and buried, often in an urn or under a burial mound.
Regional Variations
Cremation practices varied across the Viking world, influenced by local customs and available resources. In regions where wood was scarce, burials were more common.
Mound Burials
Mound burials, where the deceased were interred under earthen mounds, were another prominent Viking burial practice. These mounds served as lasting monuments to the dead.
Construction and Significance
Burial mounds were carefully constructed, with the deceased placed in a chamber along with grave goods.
These mounds marked the grave’s location and signified the deceased’s ongoing presence in the community.
Archaeological Discoveries
Sites like Lindholm Høje in Denmark have revealed extensive burial mounds, providing valuable insights into Viking burial practices and social structure.


Ground Burials
Ground burials were simpler than mound or ship burials but still carried significant meaning. These included wooden chamber burials and simple pit graves.
Simple Burials
Simple burials involved placing the body in a pit or wooden chamber, often with personal belongings. These burials reflected a more straightforward approach to honoring the dead.
Chamber Burials
Chamber burials involved constructing a wooden chamber within the grave, where the deceased was placed along with grave goods. This method was more common for those of higher status.
Funeral Rituals and Customs
Viking funerals were rich in rituals and customs, reflecting their beliefs and societal norms. These practices included the preparation of the body, communal feasts, and various forms of sacrifice.
Preparation of the Body
The preparation of the body was a critical part of the funeral process, involving special clothing and purification rites.
Clothing and Adornments
The deceased were dressed in new clothes, often specially made for the funeral. These garments symbolized a fresh start in the afterlife.
Purification Rites
Purification rites, such as washing the body, were conducted to prepare the deceased for their journey. These rites were believed to cleanse the soul and ensure a smooth transition to the afterlife.
Funeral Feasts and Gatherings
Funeral feasts were communal events, bringing together family and friends to honor the deceased and celebrate their life.


Feasting and Drinking
Feasting and drinking were central to Viking funerals. These gatherings allowed the community to pay their respects and share memories of the deceased.
Storytelling and Oral Traditions
Storytelling was an essential part of the funeral, with tales of the deceased’s life and achievements being recounted. This helped preserve their memory and reinforce cultural values.
Human and Animal Sacrifices
Sacrificial practices were a part of some Viking funerals, reflecting their beliefs about the afterlife and the need to provide the deceased with companions or servants.
Rituals and Beliefs
Human and animal sacrifices were conducted to accompany the dead into the afterlife.
These practices, though brutal, were seen as essential to ensuring the deceased had everything they needed for their journey.
Accounts by Eyewitnesses
Accounts like those of Ahmad ibn Fadlan provide detailed descriptions of these sacrificial rites, offering a rare glimpse into Viking funeral practices from an outsider’s perspective.
Grave Goods and Their Significance
Grave goods were an integral part of Viking burials, serving both practical and symbolic purposes. They reflected the deceased’s status, profession, and beliefs.
Types of Grave Goods
The types of grave goods varied widely, from weapons and tools to personal items and provisions for the afterlife.
Weapons and Tools
Weapons, such as swords and axes, were common grave goods, symbolizing the deceased’s warrior status and ensuring they were prepared for any challenges in the afterlife.
Jewelry and Personal Items
Jewelry and personal items, like brooches and combs, were also included, reflecting the deceased’s daily life and status.


Provisions for the Afterlife
Provisions such as food and drink were buried with the deceased to sustain them on their journey to the afterlife.
The Symbolism of Grave Goods
Grave goods carried deep symbolic meaning, representing the deceased’s life and beliefs.
Status and Wealth
The richness of grave goods often reflected the deceased’s status and wealth, showcasing their achievements and ensuring their memory was honored.
Religious Beliefs
Grave goods also symbolized religious beliefs, with items chosen to help the deceased navigate the afterlife and reach their final destination.
Regional Variations in Burial Practices
Viking burial practices varied significantly across different regions, influenced by local customs, resources, and the spread of Christianity.
Scandinavia
Scandinavian regions, including Norway, Denmark, and Sweden, had their own unique variations in burial practices. Each area’s customs reflected local beliefs and resources.
Norway
In Norway, ship burials were prominent among the elite, symbolizing the deceased’s journey to the afterlife.
Mound burials were also common, often accompanied by rich grave goods. Cremation was practiced but gradually declined with the spread of Christianity.
Denmark
Denmark saw a mix of cremation and inhumation burials. Mound burials were typical, with the deceased interred with significant items.
The conversion to Christianity brought changes, leading to simpler burials without grave goods over time.

Sweden
In Sweden, cremation was a prevalent practice, often followed by the burial of ashes in urns. Mound burials were also significant, with some of the largest burial mounds found in this region.
As in other parts of Scandinavia, the shift to Christianity influenced burial customs.
Influence of Christianity
The spread of Christianity across Scandinavia significantly impacted Viking burial practices, leading to a gradual shift from traditional pagan customs to Christian ones.
The Transition from Pagan to Christian Practices
The conversion to Christianity brought new burial practices, such as inhumation without grave goods and the orientation of graves facing east. Over time, these practices replaced the elaborate pagan rites.
Impact on Burial Customs
Christian influence led to the decline of cremation and the end of practices like human and animal sacrifices. The emphasis shifted to simpler burials, reflecting the new religious beliefs and customs.
Archaeological Insights
Archaeological discoveries have provided valuable insights into Viking burial practices, revealing the complexity and diversity of these ancient customs.
Major Archaeological Sites
Several key archaeological sites have shed light on Viking burial customs, offering a glimpse into their societal structure and beliefs.
Lindholm Høje
Lindholm Høje in Denmark is one of the largest and most significant Viking burial sites.
It features numerous stone ship settings and burial mounds, providing evidence of both cremation and inhumation practices.
Birka
Birka, located in Sweden, is another major site with well-preserved burial mounds.
Excavations have uncovered rich grave goods and provided insights into the influence of trade and contact with other cultures.

Jelling
The Jelling site in Denmark includes monumental burial mounds and runestones, marking the transition from pagan to Christian practices.
The site is closely associated with King Harald Bluetooth and the Christianization of Denmark.
Findings and Discoveries
Archaeological excavations at these sites have revealed much about Viking society, including their social hierarchy, beliefs, and daily life.
Significance of Excavations
The findings from Viking burial sites provide a wealth of information about their rituals, social structures, and interactions with other cultures.
These discoveries help historians and archaeologists understand the complexity of Viking life and death.
Insights into Viking Society
Grave goods, burial methods, and the locations of burials offer insights into the roles and statuses of individuals within Viking society.
They also reveal how the Vikings viewed death and the afterlife, reflecting their rich cultural heritage.
Conclusion
The death and burial customs of the Vikings were deeply intertwined with their beliefs and social structures.
These practices not only honored the deceased but also reinforced community bonds and cultural values.


The Legacy of Viking Burial Customs
Today, the legacy of Viking burial customs continues to fascinate and educate us. These ancient practices offer a window into a bygone era, revealing the complexities and richness of Viking culture.
Continuing Influence on Modern Culture
Viking burial customs have left a lasting impact on modern culture, influencing literature, art, and popular media.
Their practices continue to inspire interest and study, highlighting the enduring fascination with Viking history.
Preservation and Education
Efforts to preserve Viking burial sites and artifacts ensure that these cultural treasures remain available for future generations.
Through education and research, we can continue to uncover and appreciate the depth of Viking traditions and their contributions to our understanding of the past.











